How Beta-Alanine Boosts Endurance
Beta-alanine helps you push through fatigue and improve endurance by increasing carnosine levels in your muscles. This amino acid works as a buffer, reducing acid buildup during high-intensity exercise. Unlike quick fixes like caffeine, beta-alanine requires consistent use - 3 to 6 grams daily for 4–6 weeks - to deliver results. Here's what you need to know:
- How it works: Beta-alanine raises carnosine levels by 30–50%, delaying fatigue during activities lasting 1–10 minutes.
- Performance benefits: Recreational athletes see a 2–3% improvement, while elite athletes gain 0.5–1%.
- Dosing tips: Split daily doses (800–1,000 mg per serving) to reduce side effects like tingling.
- Best timing: Start a loading phase 4–8 weeks before high-intensity training or races.
Beta-alanine is safe when taken as directed and works best when paired with structured training. Whether you're a runner, cyclist, or HIIT athlete, this supplement can help you sustain high performance during tough workouts or competitions.
How Beta-Alanine Works in Your Body
What Beta-Alanine Does
Beta-alanine plays a key role in delaying fatigue by driving carnosine synthesis. It’s a non-essential amino acid, meaning your body can produce it, but it’s not used to build muscle proteins like leucine or lysine. Instead, beta-alanine serves as a building block for carnosine. Inside muscle cells, beta-alanine pairs with histidine (thanks to an enzyme called carnosine synthase) to create carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine). Since muscles already have plenty of histidine, it’s beta-alanine that limits how much carnosine your body can produce. Research shows that supplementing with 3–6 grams of beta-alanine daily for 4–6 weeks can increase muscle carnosine levels by 30–50%.
This synthesis is crucial for understanding how carnosine helps buffer your muscles during intense exercise.
Why Carnosine Matters for Performance
Carnosine works as an intracellular buffer, particularly in fast-twitch and mixed muscle fibers. When you push through high-intensity exercise, glycolysis (your body’s process for breaking down glucose) produces lactic acid. This leads to a buildup of hydrogen ions (H⁺), which causes muscle pH to drop from its resting level of about 7.2 to around 6.6 during exhaustion. This drop - known as muscle acidosis - contributes to the burning sensation you feel and is a major factor in fatigue. Carnosine’s imidazole ring binds these extra hydrogen ions, slowing the pH decline. This buffering action allows your muscles to keep contracting effectively during efforts that last between 1 and 10 minutes.
Benefits for Endurance Performance
The buffering power of carnosine translates into noticeable performance benefits, especially during high-intensity activities. By neutralizing hydrogen ions, carnosine helps maintain optimal enzyme activity and muscle function. Studies show that beta-alanine is particularly effective for efforts lasting 1–10 minutes, with the strongest impact in the 1–4 minute range where lactate levels spike above 10 mmol/L. For example, in one trial, athletes who supplemented with beta-alanine for six weeks saw their time to exhaustion improve from 1,168.2 seconds to 1,386.7 seconds. In comparison, the placebo group’s performance increased from 1,128.7 seconds to 1,299.6 seconds.
These results highlight beta-alanine’s benefits for high-intensity, sustained activities like middle-distance running, rowing, cycling time trials, and interval-based sports or HIIT. Even in longer endurance events, the ability to handle surges, tackle hills, or sprint to the finish can give athletes a noticeable edge.
How Beta-Alanine Boosts Endurance
Beta-Alanine Dosing Protocol and Timeline for Athletes
Dosing and Loading Protocol
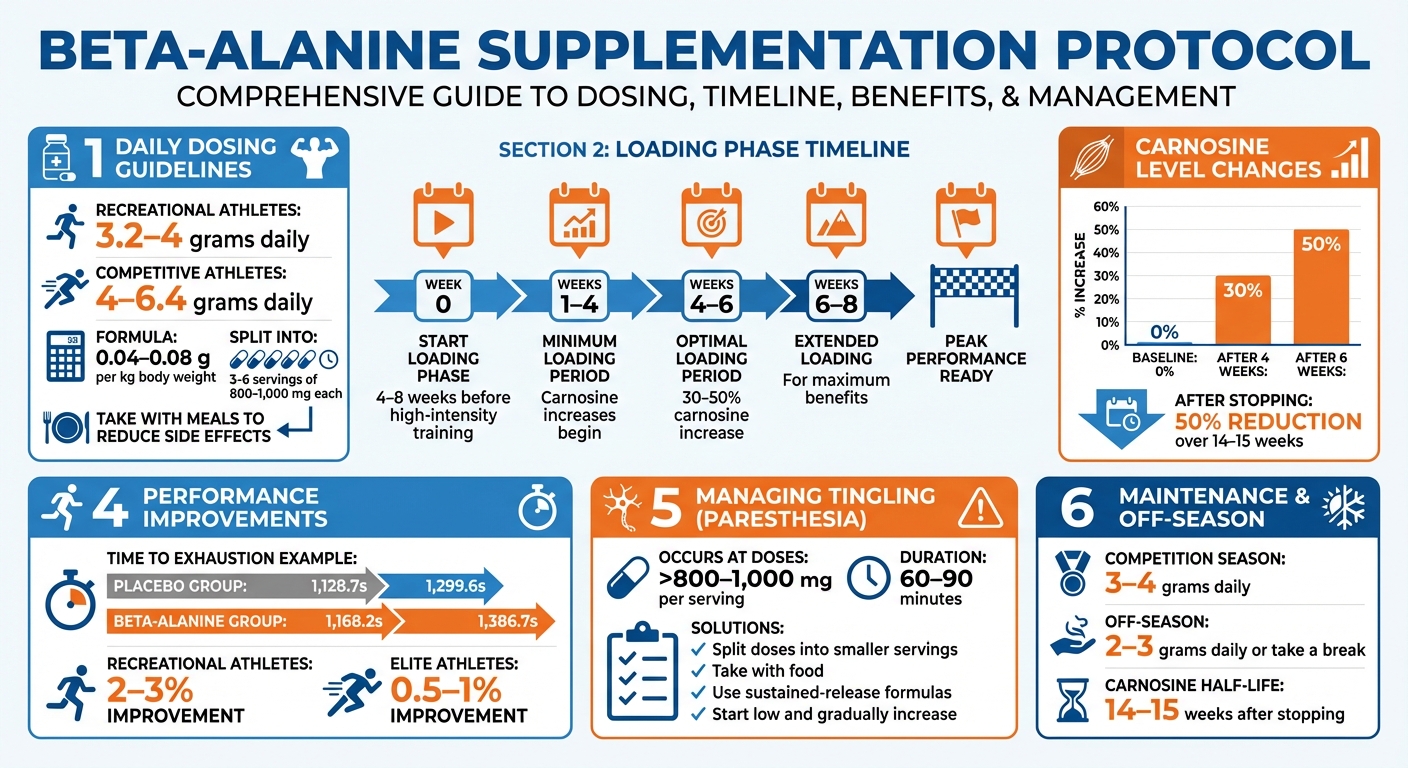
For effective results, the recommended daily dose of beta-alanine ranges from 3.2 to 6.4 grams, divided into smaller servings throughout the day. Recreational athletes can start with 3.2–4 grams daily, while competitive athletes looking to maximize carnosine levels may take 4–6.4 grams daily. A helpful rule of thumb is 0.04–0.08 g per kilogram of body weight.
Beta-alanine works through a loading phase, requiring at least 4 weeks of consistent use to significantly boost muscle carnosine levels and deliver noticeable performance benefits. Research shows that taking 3–6 grams daily for 4–6 weeks can raise muscle carnosine by 30–50%, which is linked to improved endurance. Once loaded, carnosine levels decrease gradually - it takes about 14–15 weeks to lose half of the gains after stopping supplementation. This slow decline allows athletes to plan their loading phases ahead of race seasons and still benefit even if intake is reduced later .
Unlike caffeine, beta-alanine doesn’t provide immediate effects, so flexibility in dosing is key. Most athletes divide their daily dose into 3–6 servings of 800–1,000 mg, often taking it with meals to improve absorption and reduce side effects like tingling.
Dealing with Tingling Sensations
The most common side effect of beta-alanine is paresthesia, a harmless tingling or prickling sensation. This typically occurs when single doses exceed 800–1,000 mg, with stronger sensations reported at larger doses (e.g., 2–3 grams taken at once). The tingling is often felt on the face, neck, shoulders, or hands shortly after ingestion. While it can feel intense, studies confirm that this sensation is not harmful when taking beta-alanine within the recommended dosage range.
To reduce tingling, try taking beta-alanine with food or opt for sustained-release formulations, which release the ingredient more gradually. Starting with a lower dose, such as 3.2 grams per day, and slowly increasing it over 1–2 weeks can also help your body adjust. Once you’ve fine-tuned your dosing and minimized side effects, beta-alanine can seamlessly become part of your training routine.
Using Beta-Alanine with Your Training Plan
Once dosing is sorted, it’s time to incorporate beta-alanine into your training. During base-building phases, which focus on lower-intensity mileage, start your loading phase 4–8 weeks before introducing high-intensity interval or race-pace workouts. This timing ensures your muscle carnosine levels are fully elevated when your training ramps up.
Beta-alanine shines during high-intensity efforts, especially intervals and tempo workouts lasting 1–10 minutes, where lactate buildup is a challenge. Keep up your daily dose while tackling sessions like VO₂max intervals (e.g., 3–5 minute repeats), threshold runs, long climbs, or repeated sprints. For example, a six-week interval training study found that athletes supplementing with beta-alanine increased their time to exhaustion from 1,168.2 seconds to 1,386.7 seconds, compared to the placebo group’s improvement from 1,128.7 seconds to 1,299.6 seconds.
As race day approaches, begin or refresh your loading phase 4–6 weeks before key events such as 800-meter to 5K races, cycling time trials, or HIIT competitions. During periods of frequent racing, maintaining 3–4 grams per day can help sustain elevated carnosine levels. In the off-season, you might reduce your dose to 2–3 grams daily or take a break entirely, knowing that muscle carnosine levels decrease slowly, with about a 50% reduction over 14–15 weeks.
sbb-itb-7567710
Beta-Alanine for Different Types of Athletes
Athletes in various sports face unique challenges, and beta-alanine can be a game-changer when tailored to their specific needs. By delaying fatigue and improving performance during high-intensity efforts, beta-alanine becomes a valuable tool across multiple disciplines.
For Runners
Runners tackling 5K, 10K, or half-marathon races often encounter intense moments - like surges, steep hills, or that final sprint to the finish line. These are exactly the situations where beta-alanine shines. By boosting muscle carnosine levels, it helps buffer acid buildup, allowing runners to push harder and delay fatigue during efforts lasting 1 to 10 minutes. Research suggests recreational runners may see performance improvements of about 2–3%, while elite runners might notice a more modest gain of 0.5–1%. If you’re already using a pre-workout supplement that includes beta-alanine, make sure to count it toward your daily intake. Endurance athletes in sports like cycling and triathlon can also benefit from these same effects.
For Cyclists and Triathletes
Cyclists and triathletes often face grueling time trials, steep climbs, and repeated surges that push them to their limits. In these moments, beta-alanine helps reduce the impact of lactate buildup, enabling athletes to sustain high power outputs near or above their critical thresholds. Incorporating beta-alanine during training blocks with high-intensity intervals - such as 4–6 sets of 4–5 minute efforts at 105–120% of your functional threshold power - can make a noticeable difference. Brick sessions that combine cycling and running also benefit from this supplementation. One study found that cyclists improved their 30-second sprint power by about 5% after prolonged cycling. Maintaining consistent dosing for 4–10 weeks before key races can help you recover faster between intense efforts, giving you an edge when it counts.
For Team Sports and HIIT Athletes
Athletes in team sports and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) often rely on short, explosive bursts of energy lasting 10–60 seconds, followed by brief recovery periods. Beta-alanine’s ability to buffer muscle acidity can help sustain sprint performance deeper into games and improve recovery between bursts. Stick to the dosing protocol mentioned earlier, especially during training that includes small-sided games, repeated sprint drills, or high-intensity circuits. For example, one study showed that athletes using beta-alanine during six weeks of interval training increased their time to exhaustion more than those taking a placebo. Many team sport and HIIT athletes find it convenient to add beta-alanine through a NutriFitt pre-workout supplement. Just remember to factor in the beta-alanine content of any pre-workout product when calculating your daily dose to maximize its benefits during competition.
Safety and Quality Considerations
Safety Profile and Side Effects
When it comes to beta-alanine, consistency in use is essential, but so is ensuring the product meets high standards. At recommended doses - between 3.2 and 6.4 grams per day for 4 to 12 weeks - beta-alanine has been shown to be safe. Even studies lasting up to 24 weeks found no concerning effects on blood chemistry, liver, or kidney function in healthy individuals.
One common side effect is paresthesia, a temporary tingling sensation that can occur with larger single doses (800 mg or more). This reaction happens because beta-alanine interacts with sensory neurons in the skin, but it’s not caused by nerve damage or an allergic response. The sensation usually fades within 60 to 90 minutes. To reduce this effect, you can split your daily dose into smaller portions (800–1,600 mg taken 3–4 times a day), opt for sustained-release formulations, or take beta-alanine with meals.
Certain people should consult a healthcare professional before using beta-alanine. This includes those who are pregnant, trying to conceive, or breastfeeding; anyone under 18; individuals with kidney, liver, cardiovascular, or neurological conditions; people with a history of unexplained tingling or neuropathy; and those taking multiple medications or other performance-enhancing supplements.
Choosing Quality Supplements
The quality of your supplement plays a huge role in its effectiveness and safety. To ensure you’re getting a reliable product, look for third-party testing certifications. Labels like NSF Certified for Sport or Informed-Sport confirm that the supplement is free of banned substances and contaminants, which is especially critical for competitive athletes. In the U.S., it’s also wise to check if the manufacturer complies with cGMP (current Good Manufacturing Practices) standards.
A trustworthy product will clearly state the beta-alanine dose per serving in grams, not bury it within a "proprietary blend.” If you’re using a multi-ingredient pre-workout, such as those from brands like NutriFitt, make sure the beta-alanine content is disclosed. Keep track of your total daily intake from all sources to stay within safe limits. Be cautious of products that make extreme performance claims, lack contact information, or don’t undergo third-party testing - these are warning signs of poor quality or potential mislabeling.
Conclusion
Beta-alanine offers a practical way to boost endurance by increasing muscle carnosine levels by 30–50% after consistent use for 4–6 weeks at doses of 3–6 grams daily. This increase helps buffer acid buildup during high-intensity exercise, delaying fatigue and extending performance capacity.
For the best results, aim for 3–6 grams of beta-alanine per day, divided into smaller doses to reduce the chance of tingling sensations (paresthesia). Stick to this routine for at least four weeks, though extending usage to 8–12 weeks can lead to even greater performance improvements.
While beta-alanine isn’t a quick fix, it’s a proven aid when combined with structured training like high-intensity interval sessions. It can help you push through fatigue, whether that’s shaving seconds off a race, powering through a challenging hill climb, or maintaining sprint speed during a game.
Beta-alanine is safe when taken at recommended doses. To minimize any tingling effects, consider split doses or sustained-release options. When choosing a supplement, look for clear labeling of beta-alanine content per serving and third-party testing to ensure quality.
Paired with a solid training plan, beta-alanine can help you train harder and perform longer by buffering muscle acidity and delaying fatigue. For supplements designed to support endurance, check out NutriFitt’s range.
FAQs
What makes beta-alanine unique as an endurance supplement?
Beta-alanine is known for its ability to boost muscle carnosine levels, which plays a key role in buffering lactic acid during intense workouts. By slowing the buildup of lactic acid, it helps delay fatigue, letting you train harder and for longer periods. This can lead to noticeable improvements in both endurance and overall performance.
What sets beta-alanine apart is its direct impact on muscle performance during high-intensity activities. For athletes and fitness enthusiasts looking to push their limits and build stamina, it’s a go-to supplement.
How can I reduce the tingling sensation caused by beta-alanine?
The tingling sensation - technically called paresthesia - is a harmless but often surprising side effect of beta-alanine. If it feels uncomfortable, there are a few ways to tone it down. Start with smaller doses and slowly increase the amount over time. Another approach is to divide your daily dose into smaller portions and spread them throughout the day. Taking beta-alanine alongside food can also help soften the intensity of the tingling.
How does beta-alanine help endurance athletes like cyclists and triathletes?
Beta-alanine is an effective supplement for boosting endurance in athletes, particularly during long-lasting physical activities. It achieves this by raising carnosine levels in your muscles, which helps counteract acid buildup. This process minimizes the burning sensation commonly experienced during intense workouts.
For sports like cycling or triathlons, this translates to sustaining higher effort levels for longer durations. When incorporated properly, beta-alanine can be a valuable ally in tackling challenging training sessions or competitions, helping you push past your limits and recover more efficiently.

















